If you have ever used a digital version of the Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia (link) in Bible Software you may have run across words in parenthesis. In general the words you find in Parenthesis are what are known as the קרי(Qere / read). The Qere are suggested scribal corrections of typos or errors found in Hebrew manuscripts and in the case of the BHS those found in the Leningrad Codex (link) now housed at the National Library of Russia in Saint Petersburg . The Qere is the corrected text that is to be read while the כתיב (K’tiv /writen) is what is actually written in the text before you. The Masoretes were afraid of editing the ancient manuscript so instead they added footnotes and margin notes with corrections. In general when using a digital Hebrew text you will find these ancient correction in Parenthesis. Now, Sometimes you may come across blank Parenthesis and in the case of Accordance Bible Software(link) these may be labeled/tagged as קק qq [qere blank]. You will find on these in Ruth chapter 3 verse 12.
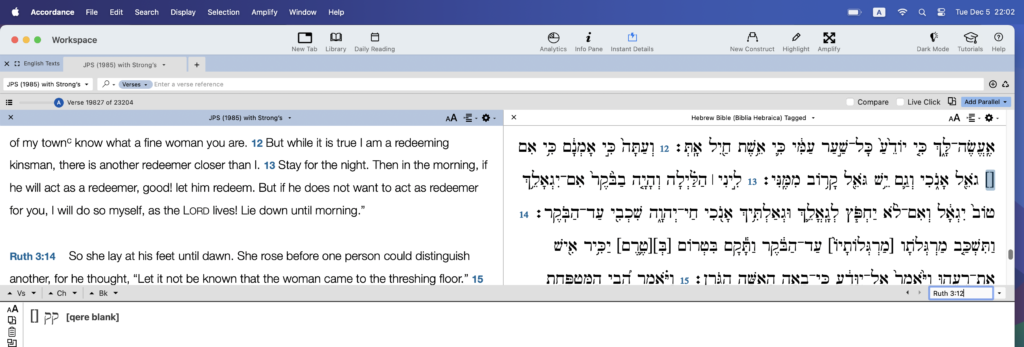
Well, what does this mean…
This means that there is no קרי(Qere / read) for the word אִם there is only the כתיב (K’tiv /writen) for אִם and furthermore other Hebrew manuscripts of Ruth from the Middle Ages also do not have a קרי(Qere) at verse 12. If you have the BHS in print turn to page 1323 look at verse 12 of Ruth chapter 3 and notice the מסורה קטנה (Masorah Katana or Parva) written on the right hand margin here by the בַּעֲלֵי הַמָּסוֹרָה (Masoretes) you will notice that they tells us that this one of 8 times were a word is to be written and not read.
Here is a picture of the Masorah Parva / Masorah Katana of the BHS on page 1323

And it reads thus….
אִם חד מן ח̇ כת̇ ולא קר̇ “The word אִם is one of 8 words which are to be written but not to be read”. Naturally, you might want to know where the other occurrences are, right. Well, you are in luck! The beautiful Accordance Masorah Thesaurus module(link) lists all 8 times of the occurrence of the ‘write not read’ phenomenon:
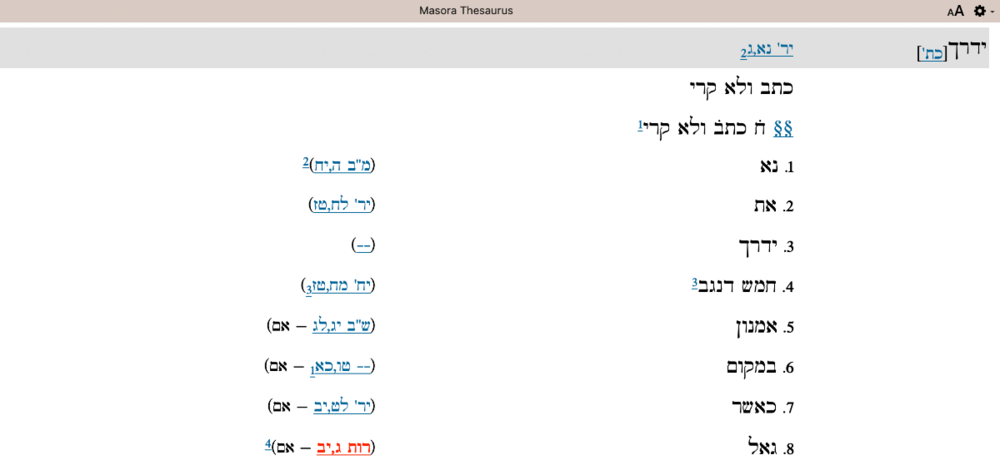
The electronic version of Weil, Gérard. E’s Massorah Gedolah: Manuscrit B. 19a de Léningrad. Rome: Pontificium Institutum Biblicum, 2001 from Logos also list all 8 occurrences. Although in a different order see:
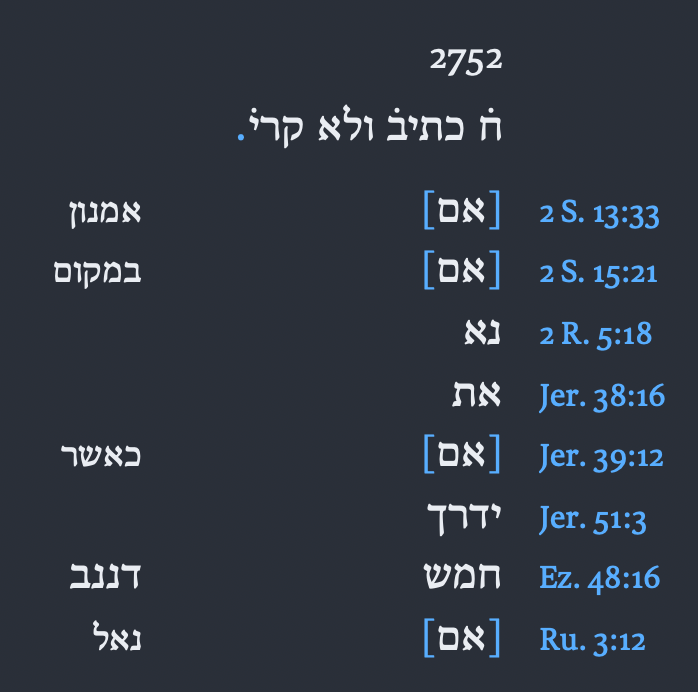
At first sight Logos’ Massorah Gedolah might look more helpful since there are some English verse references on the side, However, Accordance’s Masorah Thesaurus module has much more … so much more. For example If you enter Ruth 3:12 you will get three different list on the verse. But, that’s not all! The Masorah Thesaurus is not based only on one manuscript, rather the creators of it looked at multiple manuscripts and Masorah, on the other hand the Massorah Gedolah is based only on the Leningrad Codex and it is also a high edited version of the Leningrad codex’s Masorah. BUT, Okay, it is good, helpful and fun to have both!
Today’s post is a slightly edited version of an answer I wrote earlier this year on a thread in the Accordance Forums see: https://forums.accordancebible.com/topic/35879-qere-blank-in-hebrew/
Thanks for reading!